Building AI-Powered Applications with LangChain
Part 5 of LangChain Mastery
5/28/2025, Time spent: 0m 0s
LangChain enables developers to build context-aware, reasoning-capable AI agents and chat applications by combining powerful components. In this module, we’ll architect and implement a LangChain-powered Chat API that responds intelligently using memory, tools, and document-based knowledge.
🧠 Application Goals
- Maintain conversation memory (short-term + long-term)
- Use tools like search or calculator
- Retrieve knowledge from documents using Vector DB
- Parse output into clean formats using Output Parsers
- Demonstrate modular structure with reusability
🔧 Architecture Overview
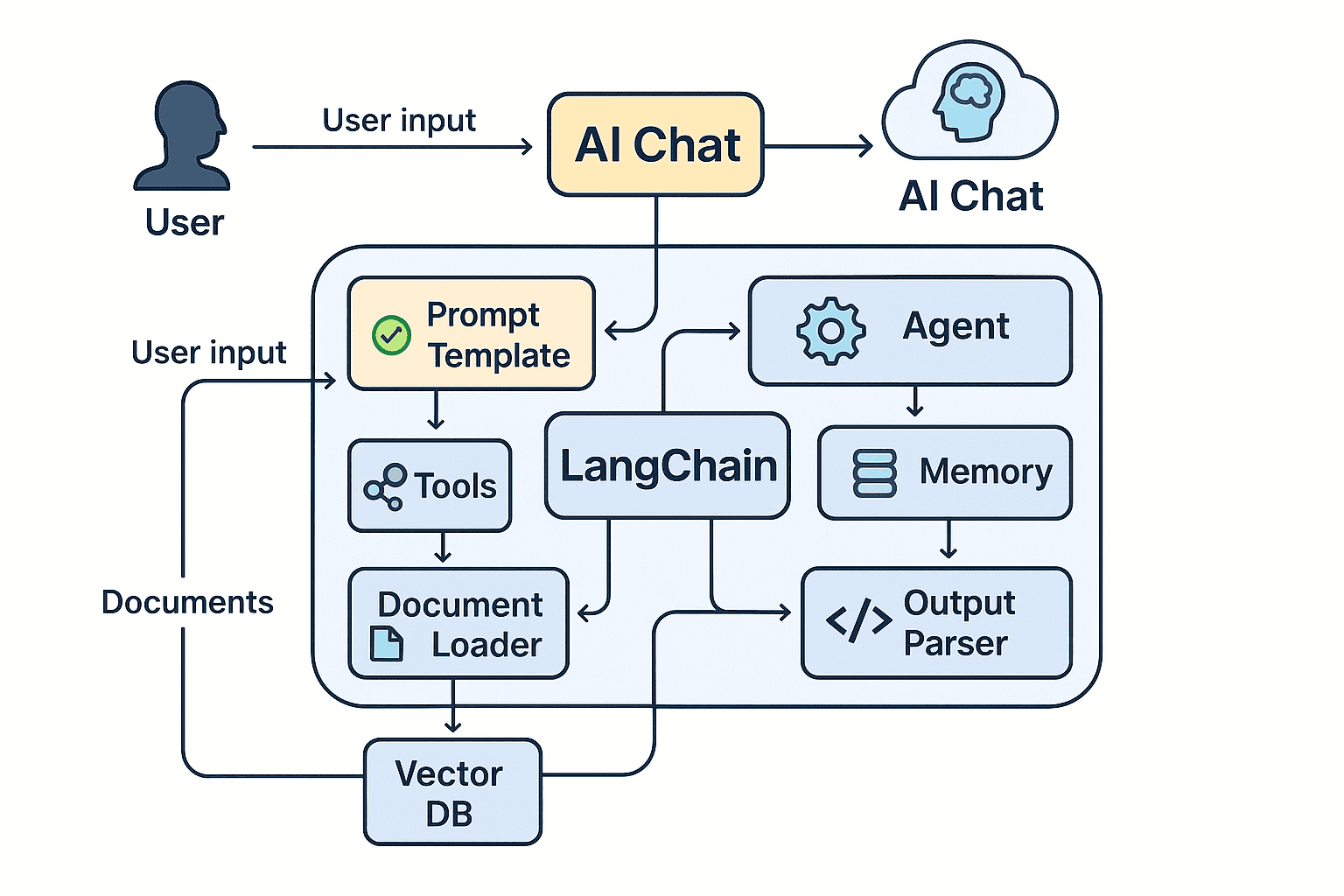
This flowchart illustrates how user inputs flow through a LangChain-based AI system:
- The Agent chooses which tools or chains to call.
- The Memory stores conversation context.
- Documents are queried via Vector Stores.
- Prompt Templates structure the LLM input/output.
📁 File Structure Breakdown
main.py
Handles the FastAPI endpoint and routes user prompts into the LangChain agent pipeline.
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from agent import agent_executor
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/chat")
async def chat(request: Request):
data = await request.json()
prompt = data.get("prompt")
response = agent_executor.run(prompt)
return {"response": response}agent.py
Sets up the LangChain agent with tools, memory, and chains.
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
from tools import tools
from memory import memory
from prompts import SYSTEM_PROMPT
from chains import qa_chain
agent_executor = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
memory=memory,
agent="chat-conversational-react-description",
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
agent_kwargs={"system_message": SYSTEM_PROMPT}
)tools.py
Defines external tools the agent can use.
from langchain.tools import Tool
from utils import search_api, calculate
tools = [
Tool(name="Search", func=search_api, description="For web queries."),
Tool(name="Calculator", func=calculate, description="Simple math.")
]memory.py
Stores short-term memory using ConversationBufferMemory.
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)prompts.py
Contains templates guiding the LLM behavior.
SYSTEM_PROMPT = "You are a helpful assistant. Always think step-by-step."chains.py
Encapsulates complex logic like Retrieval QA with a Vector Store.
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from vectordb import retriever
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(retriever=retriever, chain_type="stuff")vectordb.py
Loads documents and initializes the vector retriever.
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
loader = TextLoader("docs/sample.txt")
docs = loader.load()
db = FAISS.from_documents(docs, OpenAIEmbeddings())
retriever = db.as_retriever()🧪 Try This Locally
- Clone repo Github superml.dev Repo
- Add your OpenAI API key
- Start with
uvicorn main:app - Send POST request to
/chatwith JSON body{ "prompt": "Who is Alan Turing?" }
🚀 What You’ve Built
✅ Conversational AI agent
✅ Integrated tools and vector DB
✅ Memory-backed context
✅ Clean structured codebase
Next: Add long-term memory (Redis), advanced chaining (Multi-Input), or UI frontend!