LangChain Output Parsers: Structuring LLM Responses
by SuperML.dev,
Time spent: 0m 0s
Output Parsers in LangChain help convert raw, free-form LLM output into clean, structured, and validated formats — enabling LLMs to interact reliably with your code.
🎯 Purpose of Output Parsers
LLMs are great at generating natural language — but real-world applications need structured output:
- ✅ JSON or Python dicts for APIs
- 📋 Lists or tables for data processing
- 🧠 Named fields for semantic parsing
LangChain’s OutputParser classes bridge the gap by transforming messy text into predictable formats.
🛠️ When to Use Output Parsers
Use output parsers when:
- You need machine-readable LLM output
- You want to validate field presence or types
- You’re generating structured data like facts, summaries, metadata
- Your app logic depends on the LLM output format
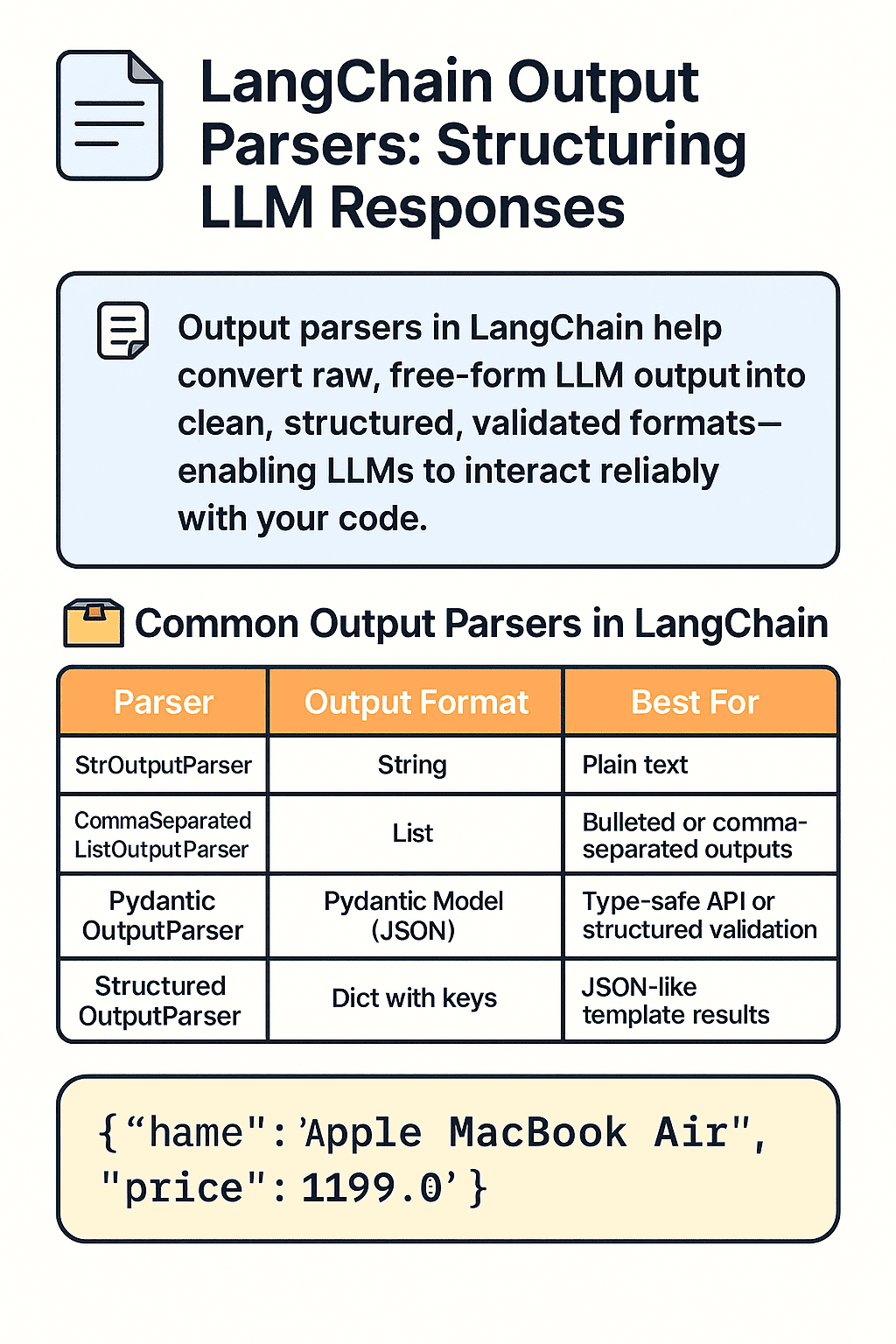
📦 Common Output Parsers in LangChain
| Parser | Output Format | Best For |
|---|---|---|
StrOutputParser | String | Plain text |
CommaSeparatedListOutputParser | List | Bulleted or comma-separated outputs |
PydanticOutputParser | Pydantic Model (JSON) | Type-safe API or structured validation |
StructuredOutputParser | Dict with keys | JSON-like template results |
🧪 Code Example: PydanticOutputParser
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
# Step 1: Define a schema
class Product(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(..., description="Name of the product")
price: float = Field(..., description="Price in USD")
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Product)
# Step 2: Create prompt
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Extract name and price from the following text:\n{text}\n{format_instructions}",
input_variables=["text"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
# Step 3: Build chain
llm = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# Step 4: Parse result
raw_output = chain.run("The Apple MacBook Air is available for $1199.")
parsed = parser.parse(raw_output)
print(parsed)✅ Output:
{
"name": "Apple MacBook Air",
"price": 1199.0
}🧠 Real-World Scenarios
- Product data extraction from reviews or articles
- Parsing user intent and entities
- Structured output for data pipelines
- LLM-driven form filling or chatbot flows
🔗 Related Posts
📘 LangChain Chains Guide 🧠 LangChain Memory Guide 🔩 LangChain Agents Guide
🚀 TL;DR
- Output Parsers convert unstructured LLM output into structured, typed data
- Useful for API responses, UI generation, or backend logic
- LangChain supports string, list, JSON, and schema-based parsers
When you want to make LLM output reliable and programmable, Output Parsers are the tool of choice.
Enjoyed this post? Join our community for more insights and discussions!
👉 Share this article with your friends and colleagues 👉 Follow us on